Connection troubleshoot
Azure Network Watcher connection troubleshoot enables you to troubleshoot network performance and connectivity issues in Azure. It provides visualization of the hop-by-hop path from source to destination, identifying issues that can potentially impact your network performance and connectivity.
Azure Network Watcher connection troubleshoot provides the following features and insights:
- A graphical topology view from your source to destination.
- It checks the connectivity between the source (VM) and the destination (VM, URI, FQDN, or IP) address.
- It offers hop-by-hop latency.
- It can identify configuration issues that are impacting reachability.
- It provides all possible hop-by-hop paths from the source to the destination.
- It checks latency (such as minimum, maximum, and average latency) between the source and destination.
- The number of packets dropped during the connection troubleshoot check.
Top Tip
Connection troubleshoot requires that the source VM has the AzureNetworkWatcherExtension VM extension installed. For installing the extension on a Windows VM, you can refer to https:// docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-machines/ extensions/network-watcher-windows?toc=/azure/ network-watcher/toc.json, and for a Linux VM, you can refer to https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/ virtual-machines/extensions/network-watcher-linux?toc=%2Fazure%2Fnetwork-watcher%2Ftoc.json.
To check network connectivity using connection troubleshoot, you have to take the following steps:
- From the Network Watcher overview blade in the Azure portal, under the Network diagnostic tools context, select Connection troubleshoot.
- Select your subscription and resource group.
- Select Virtual machine in Source type and then select your VM.
- For the Destination settings, select the Specify manually radio button, enter www.packt.com in URI, FQDN or IP address, set Protocol to TCP, and set Destination port to 80.
- Click Check. The agent will automatically be installed on the source machine when you click the check button if it is not installed already.
- Notice the success message:
Figure 18.30 – Reachable
- Try the same, this time setting Destination to a VM and selecting another VM. Set Destination port to 22. Click Check.
- Notice the failure message you receive:
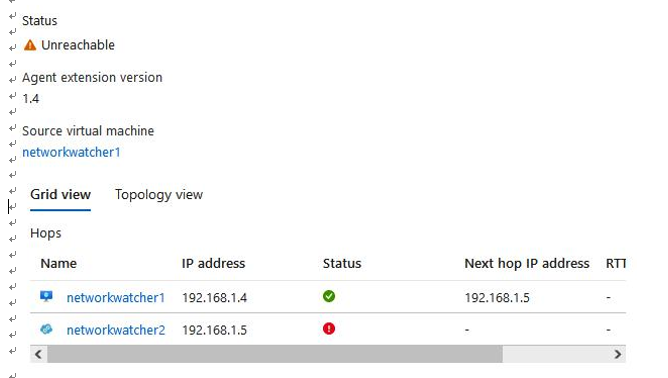
Figure 18.31 – Connection troubleshoot error
We have now checked an outbound connection from a VM using connection troubleshoot and seen both a success and failure message from the system.
Summary
In this chapter, we covered the fifth part of theConfiguring and Managing Virtual Networking objective by covering how to monitor and troubleshoot your network traffic in Azure Network Watcher. We also covered how to monitor and troubleshoot on-premises and external network connectivity using Network Watcher. You should now feel confident in not only implementing network infrastructure components within Azure but also in the monitoring and management of those services. You should be comfortable in distinguishing the difference between the various services available in Azure, and comfortable in identifying which tools you should use to troubleshoot issues on your networks using Network Watcher.
In the next chapter, we will cover some labs, and you will get to test some of your new-found skills and become more confident in working with networks in Azure.