Global peering interconnectivity Lab
This lab will guide you through creating three VNets within Azure, two in one region and one in another. The purpose of this lab is to explore inter-site connectivity through VNet peering services and confirm that you can emulate on-premises network topologies through the logical networking options available to Azure.
Estimated time: 30 minutes
Lab method: PowerShell and the Azure portal
Lab scenario: In this lab, you play the role of an administrator who is looking to emulate existing work networks that have mesh WAN links across offices using Azure. You want to confirm that you can create VNet interconnectivity, that it can span both local and regional connections, and enable similar functionality to what you have today.
Visit the following link (Lab URL) to the official Microsoft learning GitHub labs, where you will be guided through each task step by step to achieve the preceding objective.
Lab objectives:
- Task 1: Provision your environment resources (resource group, VNets, and VMs)
- Task 2: Set up VNet peering
- Task 3: Test connectivity
Lab URL: https://microsoftlearning.github.io/AZ-104-MicrosoftAzureAdministrator/Instructions/Labs/LAB_05-Implement_Intersite_Connectivity.html
Lab architecture diagram:
The following diagram illustrates the different steps involved in the exercise:
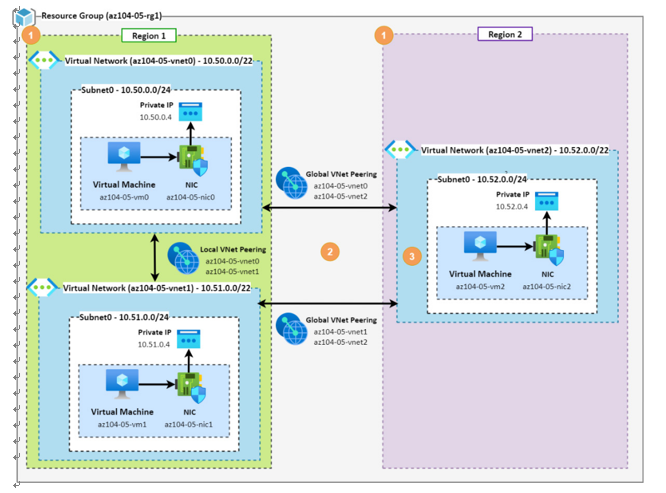
Figure 19.4 – Global peering interconnectivity – architecture diagram
After working through this lab, you should feel confident in routing traffic throughout Azure, both within the same region and across regions. You have hands-on experience working with global scale networking within Azure and should feel confident to emulate similar deployments in your daily role. The next lab will take this a step further and guide you through deploying multi-VNet infrastructure within Azure and using route tables to manage the traffic flow.
Traffic management lab
This lab will guide youthrough configuring a hub and spoke network topology, configuring route tables and user-defined routes (UDRs), and you will explore working with layer 4 and layer 7 load balancing solutions within Azure (particularly the Azure Load Balancer service and Application Gateway).
Estimated time: 60 minutes
Lab method: PowerShell and the Azure portal
Lab scenario: In this lab, you play the role of an administrator who is looking to extend upon the previous lab and confirm that traffic flow can be restricted to flowing through the hub network. You will use route tables with user-defined routes to implement the services and will validate it works as expected. Additionally, you are concerned about traffic distribution across both layer 4 and 7 load balances. You will be testing Azure Load Balancer and Application Gateway.
Visit the following link (Lab URL) to the officialMicrosoft learning GitHub labs, where you will be guided through each task step by step to achieve the preceding objective.
Lab objectives:
- Task 1: Provision your environment resources (resource group, VNets, and VMs)
- Task 2: Configure your network in a hub-and-spoke topology
- Task 3: Test VNet peering
- Task 4: Configure routing using UDRs
- Task 5: Deploy and configure load balancers
- Task 6: Deploy and configure Application Gateway
Lab URL: https://microsoftlearning.github.io/AZ-104-MicrosoftAzureAdministrator/Instructions/Labs/LAB_06-Implement_Network_Traffic_Management.html
Lab architecture diagram:
The following diagram illustrates the different steps involved in the exercise:
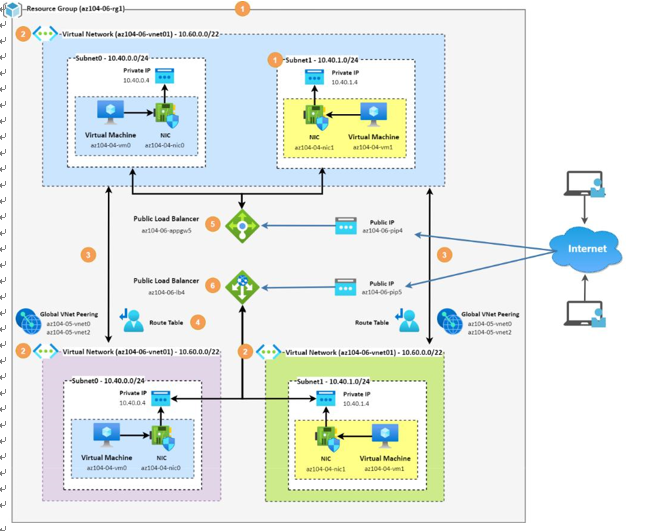
Figure 19.5 – Traffic management – architecture diagram
This lab requires eight vCPUs as the defaultconfiguration; this can be costly, and you may have a limit on the vCPU count. This can be raised but not if you are using a trial account. The demonstration will allow for single-core VMs too and you should be able to use the Standard_B1s SKU. This lab has helped you build the skills you need to deploy multi-VNet infrastructure within Azure and route traffic accordingly. You have also learned to implement load balancing services and explored how they enable you to create more resilient services.
Summary
In this chapter, we explored working with virtual networks on Azure and implementing security features such as NSGs as well as load balancers and Application Gateway. You went through a practical real-world type of scenario that you will likely encounter as an administrator. You should now feel confident in working with networks in Azure and being able to manage traffic flow effectively. It is best practice to remove unused resources to ensure that there are no unexpected costs, even though resources created in this lab do not incur additional costs.
In the next part of the book, we’ll cover the monitoring of resources within Azure, leveraging Azure Monitor.